Electric car
Electric vehicles have been considered as a replacement for fuel vehicles following the issue of increasing pollution, global warming and depletion of natural resources. In these cars, instead of using conventional propulsion methods such as internal combustion engine, electric motor and controller are used for propulsion. In these cars, electricity can be used as fuel, which can be stored in rechargeable battery packs or other energy storage devices. These batteries have limited energy capacity and need to be connected to an electrical source to recharge. The electric motor in these cars uses the electrical energy in the battery to turn the car’s wheels, causing it to move.
Although electricity generation may play a role in air pollution, electric vehicles do not emit any exhaust gases because they do not use any petroleum-based fuels, so they are considered zero-emission vehicles.

The electric car, with acceptable top speed and good acceleration, is a practical choice for everyday use and can be charged every night without incurring high costs. Of course, the limited energy capacity of the battery pack and the time it takes to recharge it compared to fossil fuels are the negative points of these cars.
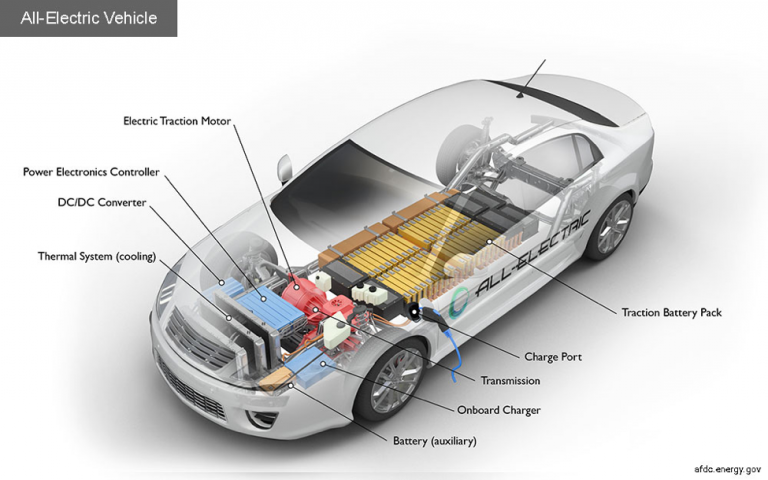
The main parts of an electric car
Auxiliary Battery: This battery provides the electricity needed for car accessories.
Charging port: This port allows the car to be connected to an external power supply to charge the battery pack.
DC.DC Converter: This component draws high DC voltage from the battery pack and converts it to DC low voltage for car accessories operation and auxiliary battery recharging.
Electric motor: This motor uses the power of the battery to move the wheels of the car. Some of these motors can be converted to generators that perform both actuator and regenerative functions.
On-Board Charger: This device converts AC input power supplied through the charging port to DC power to charge the battery pack.
Controller: This unit controls the speed of the electric motor and the torque generated by regulating the current of electrical energy received from the battery pack.
Heat management system: This system maintains a suitable operating temperature range for electric motors, electronic systems and other suitable components.
Battery pack: The electricity required for use by the electric motor is stored in this unit.
Power transmission: This unit transmits the mechanical power output from the electric motor to the wheels.